HBsAgGi ELISA Kit:
To measure HBsAg glycan isomer
An ELISA kit using monoclonal antibody to O-glycosylated PreS2 on M-HBs, allowing to measure DNA-containing viral particle.
* This product can be purchased directly from us
Applicable Genotype: C
96 Test
Product Code: RCEK-001
US$1,000.00-
Overview
A recombinant monoclonal antibody against HBsAg glycan isomer (HBsAgGi) is specific to O-glycosylated Pre-S2 on M-HBs, which are predominantly present in infectious HBV particles. Compared to traditional HBsAg-testing which recognizes all viral particles, HBV particles captured by HBsAgGi differ from those captured by S-HBsAg antibody.
By using HBsAgGi, we established for the first time a new ELISA system to measure HBV DNA-containing viral particles. Sera of HBV patient mainly contains subviral particles over the HBV DNA particles. The ratio of infectious particles vs non-infectious particles differs in each patient. Thus, measuring infectious HBV particles would be useful to analyze pathological conditions of patients.
Materials included in the kit
HBsAgGi antibody coated plate:96 well (8-well strip x 12)
Standard M-HBsAg
Dilution Buffer
HRP-labeled HBsAgGi antibody
20X Wash Buffer
TMB Substrate
Stop Solution
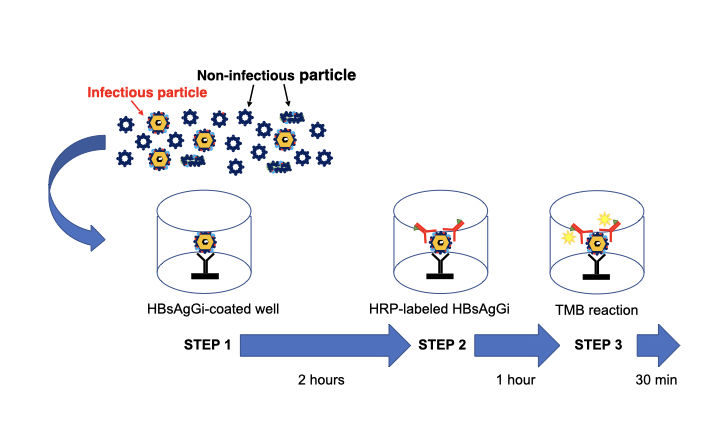
Three steps to measure HBV DNA particles by HBsAgGi ELISA Kit
HBV DNA particles can be mainly captured by HBsAgGi antibody (STEP 1). After washing, the HBV particles captured on the ELISA microwells will be further reacted with the HRP-labeled HBsAgGi antibody, (STEP 2). After further washing, HRP substrate (TMB substrate) is added into the well. After the incubation, the reaction is stopped and the absorbance at 450 nm is measured by a plate reader (STEP 3).
Examples:
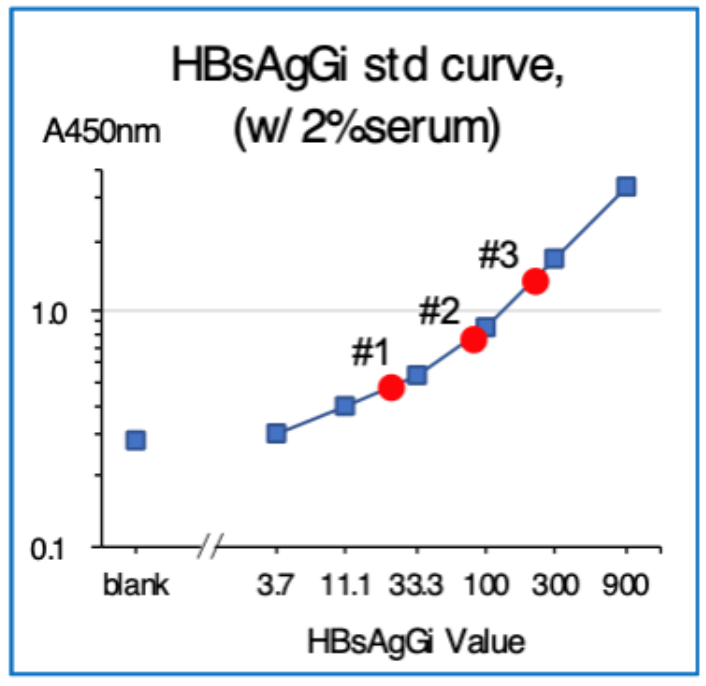
Standard curve
Standard curve was obtained by using Standard M-HBsAg included in the kit. Standard M-HBsAg (6.25 – 400 ng/mL) were obtained by serial dilution of M-HBsAg (800 ng/mL).
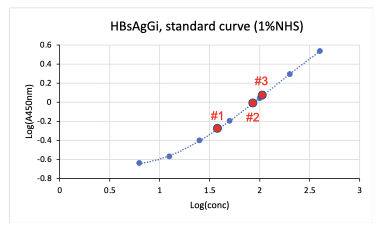
Measuring HBsAgGi in serum by using HBsAgGi ELISA kit
- Tested samples: 3 sera from patients with HBV (1 µL) were measured at 6 wells per sample.
- Standard M-HBsAg (6.25 – 400 ng/mL)
| Sample | qHBsAg (IU/mL) | HBsAgGi (µg/mL) | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum #1 | 2100 | 4.5 | 2.52 |
| Serum #2 | 8200 | 8.92 | 2.65 |
| Serum #3 | 2200 | 11.04 | 1.82 |
References:
1. Schadler and Hildt (2009) Viruses 1:185-209.
2. Schmitt et al. (2004) J Gen Virol 85:2045-2053.
3. Dobrica et al. (2020) Cells 9:1404.
4. Wagatsuma et al. (2018) Anal Chem 90:10196-10203.
5. Angata et al. (2021) Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 1866:130020

Our Distributor.
Our products can be purchased from the following distributor.
FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation
HBsAgGi:
HB surface antigen glycan isomer

A monoclonal antibody to O-glycosylated PreS2 on M-HBs, which is predominantly expressed by DNA-containing viral particle.
* This product can be purchased directly from us
Applicable Genotype: C
50μg
Product Code: RCA-001
US$700.00-
Overview
HBV envelope protein is composed of three types of surface antigens, S-, M-, and L-HBs, which are produced from an HBsAg gene containing PreS1, PreS2 and S-domains1. HBsAgs are heavily glycosylated with N-glycan and O-glycan2,3. Whole glycan structural analyses revealed that PreS2 domain on M-HBs, but not on L-HBs, contains highly conserved O-glycosylated site in genotype C (gC)4,5.
A recombinant monoclonal antibody against HBsAg glycan isomer (HBsAgGi) was generated by using O-glycosylated PreS2 peptide. Compared to traditional HBsAg-testing which recognizes all viral particles, HBsAgGi specifically recognizes infectious HBV particles (DNA virion).
⚫︎ Isotype: mouse IgG1 ⚫︎ Light chain: kappa ⚫︎ Amount: 50 μg ⚫︎ Storage: Store at –20℃ and avoid freeze / thaw cycle. Aliquots should be frozen and thawed once, with any remainder kept at 4℃ for short period.
Applications:
Western
Immunoprecipitation/Separation of HBV particles
ELISA
HBV infection inhibition assay
Immunohistochemistry
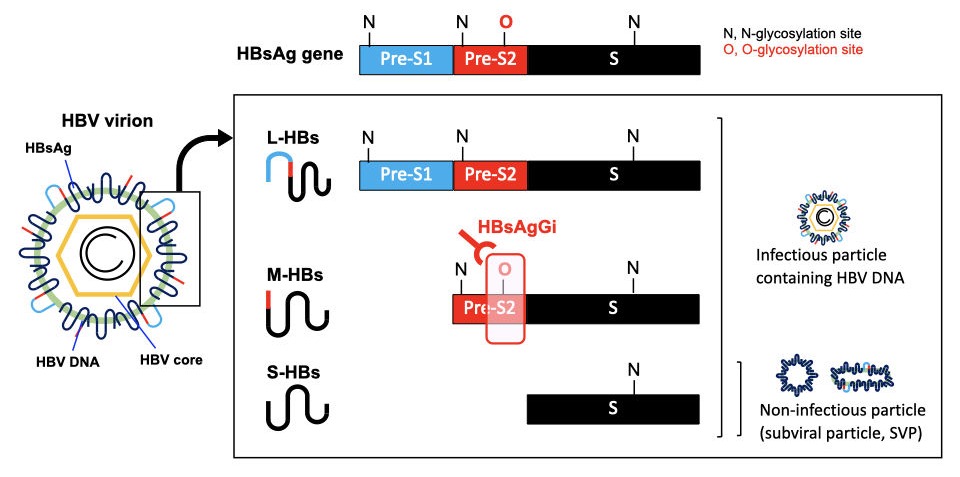
HBsAgGi specifically recognizes M-HBsAg in HBV virion
HBV virion contains envelope protein (HBsAg), HBV core and HBV DNA. HBsAg gene consists of PreS1 (blue), PreS2 (red), and S (black) -domains. About half of S-HBsAgs is modulated by N-glycan and the rest is non-glycosylated. PreS2 domain in M-HBsAg is highly O-glycosylated, but not in L-HBsAg. S-HBsAg is the most abundant and forms non-infectious particles. Infectious HBV particles consist of all HBsAgs and contains HBV DNA. HBsAgGi recognizes O-glycosylated PreS2 domain in M-HBsAg of genotype C.
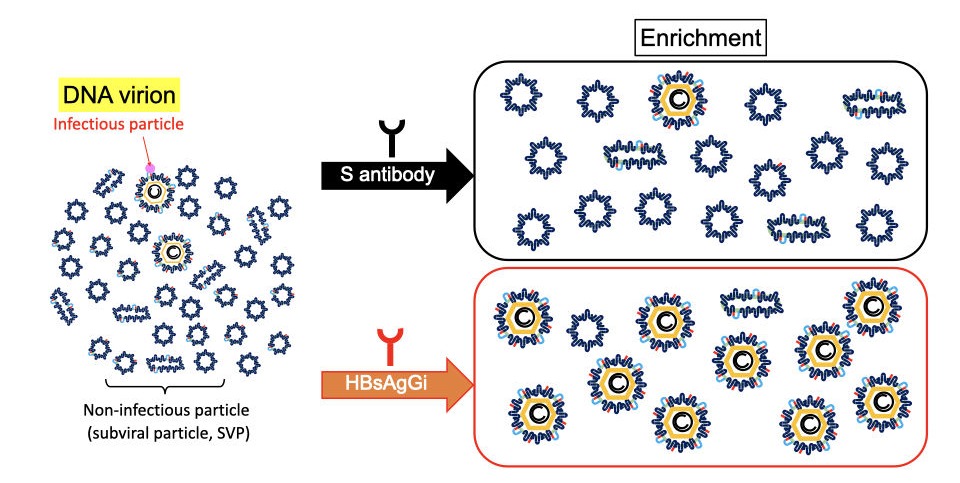
HBsAgGi antibody vs S antibody in recognition of HBV particles
In HBV patients’ serum, non-infectious particles are much dominant than infectious particles containing HBV DNA. Anti-S antibody may recognize all HBV particles including non-infectious particles, However, HBsAgGi specifically recognizes HBV particles containing M-HBsAg, resulting in efficient recognition of infectious HBV particles. HBsAgGi measuring will classify HBV patients differently from the S-antibody measuring.
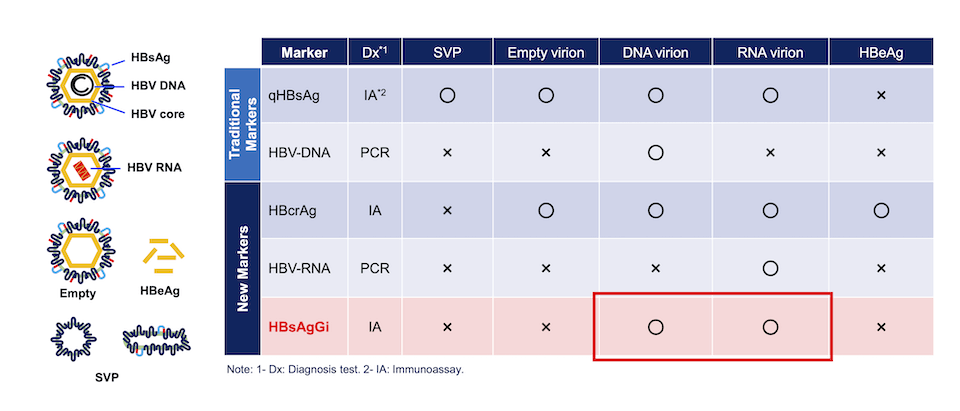
HBsAgGi and other markers to detect infectious HBV
Comparison of HBV markers. Measuring qHBsAg and HBV DNA have been used, while HBcrAg and HBV RNA are new markers to diagnose patient condition. Target HBV particles or molecules are indicated in the table. Circle (〇) indicates the target particle and molecules, and X indicates that the marker cannot recognize or not recommended.
HBsAgGi detects M-HBsAg-containing particles such as DNA or RNA virion.
Examples
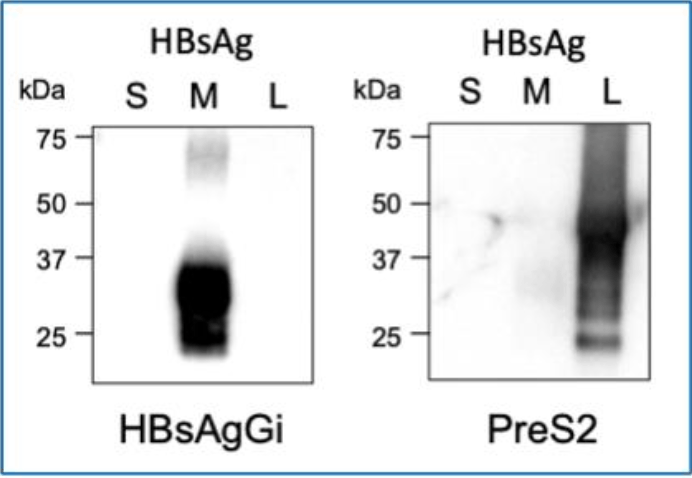
Western blotting using HBsAgGi (Left) and PreS2 antibody (Right)
- Left: HBsAgGi-gC antibody, Right: anti-PreS2 antibody
- Lane 1: S-HBsAg 50 ng
- Lane 2: M-HBsAg 50 ng
- Lane 3: L-HBsAg 50 ng
- Secondary antibody: HRP -labeled anti-mouse IgG
ELISA using HBsAgGi-gC coated plate and M-HBsAg as a standard sample
- Standard material: M-HBsAg (3.7 – 900 ng/mL)
- Tested samples: sera from patients with HBV (2 μL)
- Serum #1: HBsAg 6610 IU/mL, HBV DNA 3.1
- Serum #2: HBsAg 8612 IU/mL, HBV DNA 0
- Serum #3: HBsAg 36600 IU/mL, HBV DNA 8.3
- Detection: Biotinylated HBsAgGi-gC antibody and HRP-labeled streptavidin
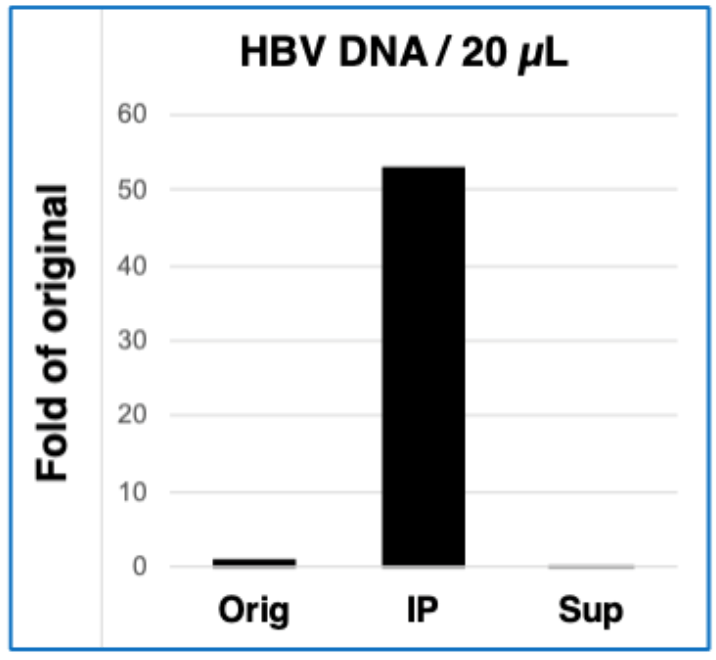
Immunoprecipitation using HBsAgGi-gC
- Original sample (Orig): HBV patient serum (4.1 logIU/20 μL)
- IP condition: Biotinylated HBsAgGi-gC 2 μg, Streptavidin-conjugated magnetic
- beads 10 μL/1 mL TBS-T, 4°C, 16 hours
- Quantification of HBV DNA: HBV DNA per 20 μL from precipitated fraction (IP) and supernatant fraction (Sup) was measured by real-time PCR method.
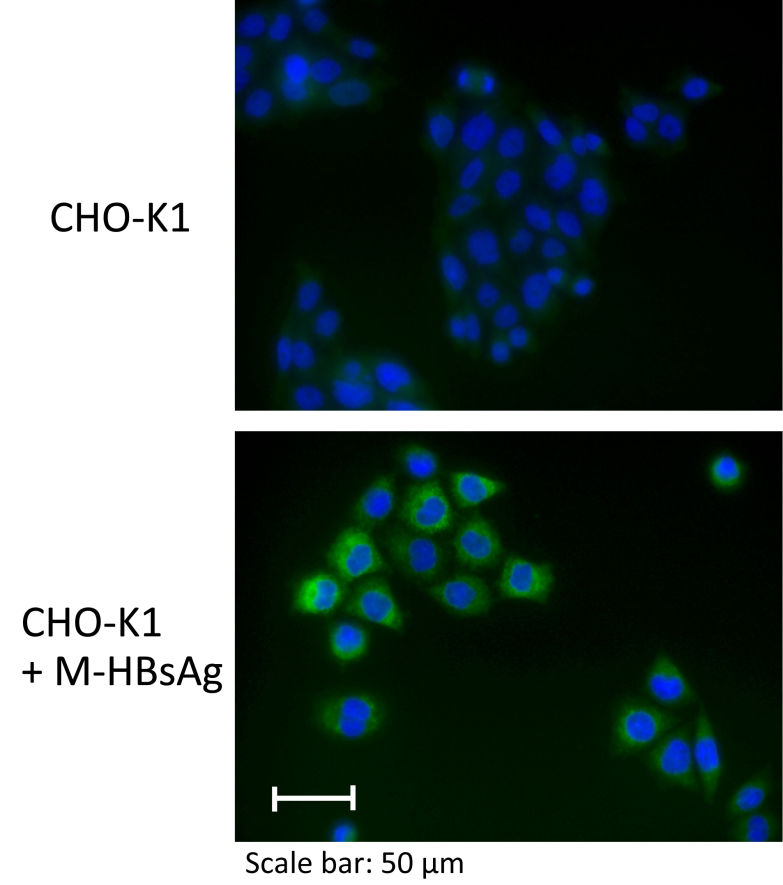
Immunostaining by HBsAgGi antibody against O glycosylated M-HBsAg
- Cell lines:CHO-K1 (Parental cell line) CHO-K1 + M-HBsAg (Stable transfectant cell line expressing M-HBsAg of genotype C, a source of standard molecule)
- 1st antibody: x100 diluted HBsAgGi in 1% normal goat serum and 0.2% saponin
- 2nd antibody:4 µg/mL AlexaFluor488 anti mouse IgG in 1% normal goat serum and 0.2% saponin
- Nuclear staining:10 µg/mL Hoechst 33342
- Intracellular staining of HBsAgGi was observed only in CHO K1 expressing M-HBsAg (Lower).
References:
1. Schadler and Hildt (2009) Viruses 1:185-209.
2. Schmitt et al. (2004) J Gen Virol 85:2045-2053.
3. Dobrica et al. (2020) Cells 9:1404.
4. Wagatsuma et al. (2018) Anal Chem 90:10196-10203.
5. Angata et al. (2021) Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 1866:130020

Our Distributor
Our products can be purchased from the following distributor.
FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation


