Latest News
2025.1.31
RCMG Inc. is pleased to announce that the results of research using the “HBsAgGi ELISA” kit, which is available from our company, have been published in the Antiviral Research by Dr. Bilian Yao and Dr. Xinxin Zhang of Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine.
Paper Title:
Serum O-glycosylated HBsAg levels correlate with HBV RNA in HBeAg positive CHB patients during antiviral therapy
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39788207/
2024.8.20
RCMG Inc. is pleased to announce that the results of research using the “HBsAgGi ELISA” kit, which is available from our company, have been published in the Hepatology Research by Dr. Taiki Okumura and Prof. Takeshi Umemura of Shinshu University School of Medicine.
Paper Title:
Hepatitis B surface antigen glycan isomer as a new potential biomarker in patients with hepatitis B virus infection.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39163253/
2024.5.28
RCMG Inc. is pleased to announce that the results of research using the “HBsAgGi ELISA” kit, which is available from our company, have been published in the Hepatology Research by Dr. Yuji Ikeda and Prof. Takuya Genda of Juntendo University Shizuoka Hospital.
Paper Title:
Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) glycan isomer is predictive of HBsAg seroclearance in patients with chronic hepatitis B.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38804859/
2024.4.12
RCMG Inc. is pleased to announce that the poster describing on the correlation of HBsAgGi (HB surface antigen glycan isomer) with HBV-DNA and HBV-RNA virions in clinical samples was presented and received the Investigator Award at the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver (APASL) Annual Meeting 2024 (Kyoto, Mar. 27-31, 2024).
Presentation No.:101368
Title:HBV surface antigen glycan isomer (HBsAgGi), correlates with HBV-DNA and HBV-RNA virions/
2024.2.7
RCMG Inc. is pleased to announce that the results of research using the “HBsAgGi ELISA” kit, which is available from our company, have been published in the Hepatology Research by Dr. Ritsuzo Kozuka and Dr. Masaru Enomoto of Osaka Metropolitan University.
Paper Title:
Hepatitis B surface antigen glycan isomer is a predictor of the development of hepatocellular carcinoma during nucleoside/nucleotide analog therapy
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38323994/
2024.2.1
RCMG Inc. is pleased to announce that the abstract on the correlation of HBsAgGi (HB surface antigen glycan isomer) with HBV-DNA and HBV-RNA virions in clinical samples has been accepted for the poster presentation at the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver (APASL) Annual Meeting 2024 (Kyoto, Mar. 27-31, 2024).
2024.1.3
RCMG Inc. is pleased to announce the publication of a review article, describing RCMG’s HBsAgGi ELISA kit, in Pathogens. Dr. Ivana Lazarevic and colleagues at University of Belgrade published a review on hepatitis B surface antigen isoforms. In this review, the HBsAgGi ELISA is presented as a potential biomarker for monitoring HBV infection.
Paper Title:
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Isoforms: Their Clinical Implications, Utilisation in Diagnosis, Prevention and New Antiviral Strategies
2023.11.10
RCMG Inc. is pleased to announce that the poster of the biochemical characteristics of HBsAgGi (HB surface antigen glycan isomer) and measuring HBsAgGi of clinical samples was presented at the AASLD The Liver Meeting® 2023 (Boston, Nov. 10-14, 2023).
Title: Hepatitis B virus surface antigen glycan isomer (HBsAgGi) as a new glyco-biomarker to detect infectious HBV virions
2023.8.8
RCMG Inc. is pleased to announce that the abstract of the biochemical characteristics of HBsAgGi (HB surface antigen glycan isomer) and measuring HBsAgGi of clinical samples has been accepted for the poster presentation at the AASLD The Liver Meeting® 2023 (Boston, Nov. 10-14, 2023).
2023.7.21
We are pleased to announce that the results of research using the “HBsAgGi ELISA” kit, which is available from our company, have been published in the Journal of Viral Hepatitis by Dr. Taiki Okumura and Prof. Takeshi Umemura of Shinshu University.
Paper Title:
Serum Kinetics of serum O-glycosylated M-hepatitis B surface antigen with hepatocellular carcinoma history and nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy in hepatitis B patients
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37363934/
In this paper, 124 chronic hepatitis B patients, including 2 asymptomatic carriers, 10 inactive carriers, 97 chronic hepatitis, and 15 cirrhosis, were studied for the clinical significance of serum HBsAgGi levels, and the following findings were reported.
- In a cross-sectional cohort analysis (Study 1, n=124), serum HBsAgGi levels were shown to be significantly correlated with serum HBV-DNA levels (p=0.001).
- Multiple logistic regression analysis in Study 1 indicated that high HBsAgGi and low HBsAgGi were independent factors associated with history of HCC (HR: 4.20, p=0.014).
- Among the chronic hepatitis patients in Study 1, 36 patients whose serum samples were analyzed before (baseline) and 48 weeks after nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy (Study 2) showed that serum HBsAgGi levels were significantly decreased after 48 weeks of treatment compared to baseline values (p<0.001).
Based on the results, the paper discusses the potential usefulness of HBsAgGi as a novel biomarker for evaluating the pathogenesis of chronic hepatitis B, both for predicting HCC onset and for evaluating disease status of patients during nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy.
2023.6.19
RCMG Inc. is pleased to announce two presentations by our customers regarding studies using HBsAgGi*1 ELISA Kit at the 59th Annual Meeting of the Japan Society of Hepatology (Nara, June 15-16, 2023).
Website (Japanese only)
https://site2.convention.co.jp/jsh59/
*1:HBsAgGi (HB surface antigen glycan isomer) A recombinant monoclonal antibody against HBsAg glycan isomer (HBsAgGi) was generated by using O-glycosylated PreS2 peptide. Compared to traditional HBsAg-testing which recognizes all viral particles, HBsAgGi specifically recognizes infectious HBV particles (DNA virion).
HBsAgGi antibody and HBsAgGi ELISA kit, which can measure infectious HBV particles described above are now available for research use only and can be purchased from RCMG Inc. and our distributor, FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation. More detail information is available at our Projects and Research Products page.
2023.6.14
RCMG, Inc. is pleased to announce the content of poster presentation of the HBsAgGi*1 at the EASL Congress 2023 (Vienna, Austria, 21-24 June 2023).
Poster number : 257-FRI
Title: A new glyco-biomarker for measuring infectious hepatitis B virus targeting surface antigen glycan isomer (HBsAgGi)
https://www.easlcongress.eu/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/EASL_2023_Congress_Abstracts_version1_6June.pdf
EASL Congress 2023 webpage: https://www.easlcongress.eu/
*1:HBsAgGi (HB surface antigen glycan isomer)
A recombinant monoclonal antibody against HBsAg glycan isomer (HBsAgGi) was generated by using O-glycosylated PreS2 peptide. Compared to traditional HBsAg-testing which recognizes all viral particles, HBsAgGi specifically recognizes infectious HBV particles (DNA virion).
Products Page
2023.4.11
RCMG Inc. is pleased to announce that the abstract of the biochemical characteristics and pilot clinical results of HBsAgGi has been accepted for the poster presentation at the EASL Congress 2023 (Vienna, Austria, 21-24 June 2023).
EASL CONGLESS 2023
https://easl.eu/
2022.12.14
RCMG Inc. is pleased to announce that it has filed to the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare for approval to manufacture and market “HBsAgGi*1 Assay Kit” as an in vitro diagnostic product in Japan.
This product is intended to measure infectious HBV-DNA-containing particles and is planned to be used in assisting the diagnosis of HBV-infectious status of chronic hepatitis B patients and in monitoring their treatment and progress.
*1:HBsAgGi (HB surface antigen glycan isomer)
A recombinant monoclonal antibody against HBsAg glycan isomer (HBsAgGi) was generated by using O-glycosylated PreS2 peptide. Compared to traditional HBsAg-testing which recognizes all viral particles, HBsAgGi specifically recognizes infectious HBV particles (DNA virion).
Products Page
References:
1. Murata A, Angata K, Sogabe M, et al. Serum O-glycosylated hepatitis B surface antigen levels in patients with chronic hepatitis B during nucleos(t)ide analog therapy. BMC Gastroenterol. 22: 270, 2022.
2. Angata K, Wagatsuma T, Togayachi A, et al. O-glycosylated HBsAg peptide can induce specific antibody neutralizing HBV infection. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 186: 130020, 2022.
2022.6.16
RCMG Inc. is pleased to announce that the first clinical study paper for HBsAgGi ELISA, entitled “Serum O-glycosylated hepatitis B surface antigen levels in patients with chronic hepatitis B during nucleos(t)ide analog therapy” has been published in BMC Gastroenterology (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35641912/).
The new study aimed to evaluate serum HBsAgGi levels in 47 patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) treated with nucleos(t)ide analogs (NAs).
Comparison of HBsAgGi levels with other markers (HBV-DNA, HBsAg, and HBcrAg) at the baseline and after 48 weeks of NA therapy demonstrated that the HBsAgGi levels significantly correlated with HBV-DNA. Both HBV-DNA and HBsAgGi levels were decreased after 48 weeks of NA therapy, indicating HBsAgGi as a novel potential biomarker to monitor infectious HBV particles in patients receiving NA therapy. Immunoprecipitation assays demonstrated that the HBsAgGi antibody can enrich HBV particles containing HBV-RNA as well as HBV-DNA. Thus, the paper indicates the usefulness of the HBsAgGi in clinical study of HBV.
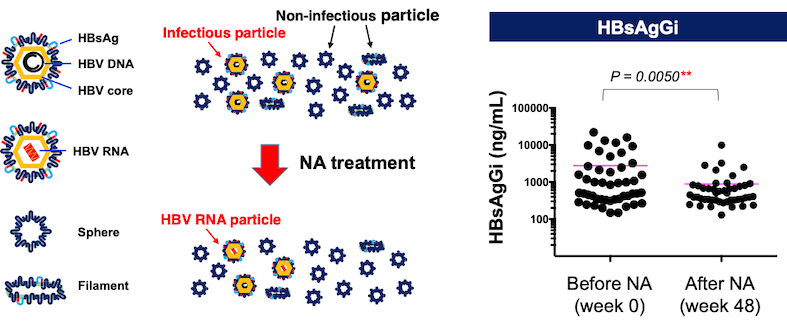
*Our research team previously found that the HBsAgGi (HB surface antigen glycan isomer) antibody is a monoclonal antibody specific to O-glycosylated PreS2 on M-HBs, which is predominantly expressed by HBV-DNA-containing viral particles.
“O-glycosylated HBsAg peptide can induce specific antibody neutralizing HBV infection”
Angata et al. (2021) Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 1866:130020
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34582939/
HBsAgGi antibody and HBsAgGi ELISA kit, which can measure infectious HBV particles described above are now available for research use only and can be purchased from RCMG Inc. and our distributor, FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation.
More detail information is available at our Projects and Research Products page.
2022.5.11
RCMG Inc. (Location: 2-1-6 Sengen, Plaza suite 209, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0047, Japan) has signed a sales contract for reagents, etc. in Japan and overseas with FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation (Head Office Location: 1-2 Doshomachi 3-Chome, Chuo-ku, Osaka 540-8605, Japan).
■FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation
Company Name: FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation
Representative Director: President Kazuo Shiraki
Head Office: 1-2 Doshomachi 3-Chome, Chuo-ku, Osaka 540-8605, Japan
Founded: 1922
Scope of Business: Providing laboratory chemicals, specialty chemicals and diagnostic reagents
Inquiries
RCMG Inc.
Email: marketing@medglyco.com
FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation
Email: ffwk-labchem-tec@fujifilm.com


