Quantifying HBsAgGi: To measure levels of HBsAg glycan isomer

An analysis service using HBsAgGi ELISA system for the first time measuring O-glycosylated M-HBsAg.
An analysis service using HBsAgGi ELISA system
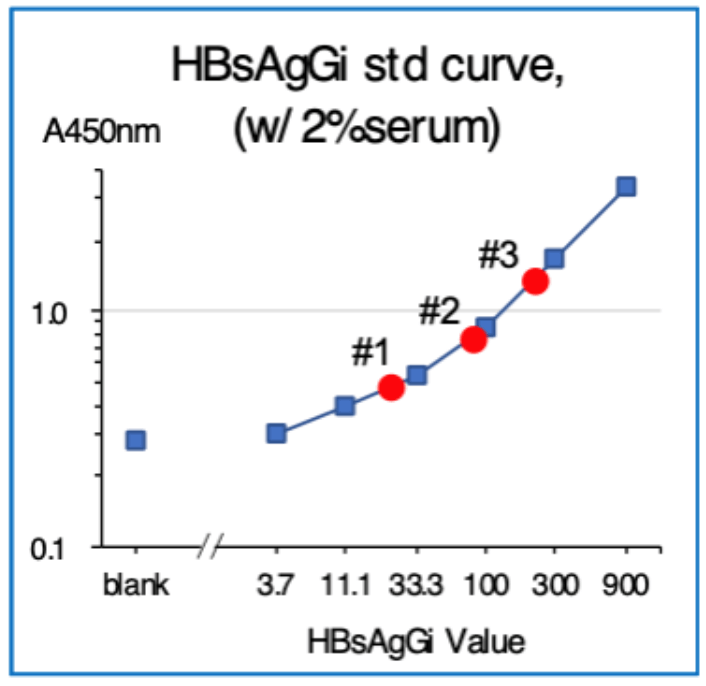
ELISA using HBsAgGi-gC coated plate and M-HBsAg as a standard sample
Standard material: M-HBsAg (3.7 – 900 ng/mL)
Tested samples: sera from patients with HBV (2 μL)
Serum #1: HBsAg 6610 IU/mL, HBV DNA 3.1
Serum #2: HBsAg 8612 IU/mL, HBV DNA 0
Serum #3: HBsAg 36600 IU/mL, HBV DNA 8.
Detection: Biotinylated HBsAgGi-gC antibody and HRP-labeled streptavidin
An analysis service of ELISA system Features
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Overview | HBV virion is covered by envelope protein (HBsAg). HBsAg is modified with N- and O-glycan in subtype-specific manner (1, 2). Three types of surface antigens, S-, M-, and L-HBsAg, which are produced from an HBsAg gene containing PreS1, PreS2 and S-domains. Infection virion contain all three HBsAgs, but non-infectious particles mainly contain S-HBsAg. For the current diagnosis or analysis of HBsAg, antibodies against S-HBsAg are used to measure amount of HBsAg. RCMG’s HBsAgGi (HBsAg glycan isomer) is a monoclonal antibody specific to O-glycosylated Pre-S2 on M-HBsAg that is included in infectious HBV containing HBV DNA (3). The particles recognized by HBsAgGi differ from the particles recognized by S-HBs antibody. Patients have less infectious HBV particles than noninfectious particles and the ration of both particles differ in each patient. Thus, measuring infectious HBV particles could be useful to analyze pathological conditions of patients. For this purpose, we established HBsAgGi ELISA system. |
| Cost | Contact Us |
| Applicable Genotype: | Applicable Genotype: B and C |
| How to order | How to Order |
| Leaflet | Leaflet |
| Safety data sheet | Safety data sheet [JP] Safety data sheet [EN] |
| User Guide | User Guide |
| References: | 1. Schmitt et al. (2004) J Gen Virol 85:2045-2053. 2. Dobrica et al. (2020) Cells 9:1404. 3. Angata et al. (2021) Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 1866:130020 |


